一、window与linux系统时间介绍
二、Linux系统时间的设置
//查看时间[root@localhost ~]# date2008年 12月 12日 星期五 14:44:12 CST//修改时间[root@localhost ~]# date --set "1/1/09 00:01" <== (月/日/年时:分:秒) 2009年 01月 01日 星期四 00:01:00 CST//date 有几种时间格式可接受,这样也可以设置时间:[root@localhost ~]# date 012501012009.30 <== 月日时分年.秒 2009年 01月 25日 星期日 01:01:30 CST
//查看硬件时间 可以是用 hwclock ,hwclock --show 或者 hwclock -r[root@localhost ~]# hwclock --show 2008年12月12日 星期五 06时52分07秒 -0.376932 seconds//设置硬件时间[root@localhost ~]# hwclock --set --date="1/25/09 00:00" <== 月/日/年时:分:秒 [root@localhost ~]# hwclock 2009年01月25日 星期日 00时00分06秒 -0.870868 seconds
//以系统时间为基准,修改硬件时间[root@localhost ~]# hwclock --systohc <== sys(系统时间)to(写到)hc(Hard Clock) [root@localhost ~]# hwclock -w//以硬件时间为基准,修改系统时间[root@localhost ~]# hwclock --hctosys [root@localhost ~]# hwclock -s
http://ntp.isc.org/bin/view/Servers/NTPPoolServers
| IP | Location | |
| 210.72.145.44 | 210.72.145.44 | 中国(国家授时中心) |
| 133.100.11.8 | 133.100.11.8 | 日本(福冈大学) |
| time-a.nist.gov | 129.6.15.28 | NIST,Gaithersburg,Maryland |
| time-b.nist.gov | 129.6.15.29 | NIST,Gaithersburg,Maryland |
| time-a.timefreq.bldrdoc.gov | 132.163.4.101 | NIST,Boulder,Colorado |
| time-b.timefreq.bldrdoc.gov | 132.163.4.102 | NIST,Boulder,Colorado |
| time-c.timefreq.bldrdoc.gov | 132.163.4.103 | NIST,Boulder,Colorado |
| utcnist.colorado.edu | 128.138.140.44 | UniversityofColorado,Boulder |
| time.nist.gov | 192.43.244.18 | NCAR,Boulder,Colorado |
| time-nw.nist.gov | 131.107.1.10 | Microsoft,Redmond,Washington |
| nist1.symmetricom.com | 69.25.96.13 | Symmetricom,SanJose,California |
| nist1-dc.glassey.com | 216.200.93.8 | Abovenet,Virginia |
| nist1-ny.glassey.com | 208.184.49.9 | Abovenet,NewYorkCity |
| nist1-sj.glassey.com | 207.126.98.204 | Abovenet,SanJose,California |
| nist1.aol-ca.truetime.com | 207.200.81.113 | TrueTime,AOLfacility,Sunnyvale,California |
| nist1.aol-va.truetime.com | 64.236.96.53 | TrueTime,AOLfacility,Virginia |
[root@linux ~]# ntpdate [-nv] [NTP IP/hostname] [root@linux ~]# ntpdate 192.168.0.2[root@linux ~]# ntpdate time.ntp.org
0 12 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate 192.168.0.1
1./etc/ntp.conf:这个是NTP daemon的主要设文件,也是 NTP 唯一的设定文件。2./usr /share/zoneinfo/:在这个目录下的文件其实是规定了各主要时区的时间设定文件,例如北京地区的时区设定文件在 /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Beijing 就是了。这个目录里面的文件与底下要谈的两个文件(clock 与localtime)是有关系的。3./etc/sysconfig/clock:这个文件其实也不包含在NTP 的 daemon 当中,因为这个是 linux 的主要时区设定文件。每次开机后,Linux 会自动的读取这个文件来设定自己系统所默认要显示的时间。4./etc /localtime:这个文件就是“本地端的时间配置文件”。刚刚那个clock 文件里面规定了使用的时间设置文件(ZONE) 为 /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Beijing ,所以说,这就是本地端的时间了,此时, Linux系统就会将Beijing那个文件另存为一份 /etc/localtime文件,所以未来我们的时间显示就会以Beijing那个时间设定文件为准。5. /etc/timezone:系统时区文件
[root@linux ~]# vi /etc/ntp.conf # 1. 关于权限设定部分 # 权限的设定主要以 restrict 这个参数来设定,主要的语法为: # restrict IP mask netmask_IP parameter # 其中 IP 可以是软件地址,也可以是 default ,default 就类似 0.0.0.0 # 至于 paramter 则有: # ignore :关闭所有的 NTP 联机服务 # nomodify:表示 Client 端不能更改 Server 端的时间参数,不过, # Client 端仍然可以透过 Server 端来进行网络校时。 # notrust : # noquery :不提供 Client 端的时间查询 # notrap :不提供trap这个远程事件登入 # 如果 paramter 完全没有设定,那就表示该 IP (或网域)“没有任何限制” restrict default nomodify notrap noquery # 关闭所有的 NTP 要求封包 restrict 127.0.0.1 #这是允许本级查询 restrict 192.168.0.1 mask 255.255.255.0 nomodify #在192.168.0.1/24网段内的服务器就可以通过这台NTP Server进行时间同步了 # 2. 上层主机的设定 # 要设定上层主机主要以 server 这个参数来设定,语法为: # server [IP|HOST Name] [prefer] # Server 后面接的就是我们上层 Time Server 啰!而如果 Server 参数 # 后面加上 perfer 的话,那表示我们的 NTP 主机主要以该部主机来作为 # 时间校正的对应。另外,为了解决更新时间封包的传送延迟动作, # 所以可以使用 driftfile 来规定我们的主机 # 在与 Time Server 沟通时所花费的时间,可以记录在 driftfile # 后面接的文件内,例如下面的范例中,我们的 NTP server 与 # cn.pool.ntp.org联机时所花费的时间会记录在 /etc/ntp/drift文件内 server 0.pool.ntp.org server 1.pool.ntp.org server 2.pool.ntp.org server cn.pool.ntp.org prefer #其他设置值,以系统默认值即可 server 127.127.1.0 # local clock fudge 127.127.1.0 stratum 10driftfile /var/lib/ntp/drift broadcastdelay 0.008keys /etc/ntp/keys
# grep "^server" /etc/ntp.conf server 0.pool.ntp.org server 1.pool.ntp.org server 2.pool.ntp.org server pool.ntp.org server 127.127.1.0 # local clock
# ntpq -pn remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter ============================================================================== 64.25.87.54 128.118.25.5 2 u 10 64 17 79.194 -542.89 1.942 64.72.116.51 129.7.1.66 2 u 9 64 17 51.569 -532.23 1.803 64.72.116.50 129.7.1.66 2 u 11 64 17 51.417 -516.70 1.417 64.72.116.45 129.7.1.66 2 u 7 64 17 51.586 -532.36 1.135 *127.127.1.0 LOCAL(0) 10 l 3 64 17 0.000 0.000 0.001
# ntpstat synchronised to local net at stratum 11 time correct to within 949 ms polling server every 64 s
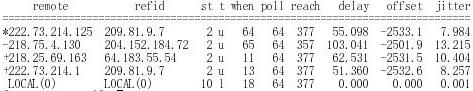
# ntpq -pn remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter ============================================================================== +64.25.87.54 128.118.25.5 2 u 56 64 377 78.548 250.871 37.180 +64.72.116.51 129.7.1.66 2 u 58 64 377 51.551 268.538 36.817 *64.72.116.50 129.7.1.66 2 u 58 64 377 51.539 274.497 36.629 +64.72.116.45 129.7.1.66 2 u 49 64 377 51.485 271.750 37.841 127.127.1.0 LOCAL(0) 10 l 44 64 377 0.000 0.000 0.001 # ntpstat synchronised to NTP server (64.72.116.50) at stratum 3 time correct to within 263 ms polling server every 64 s
# grep "^server" /etc/ntp.conf server time-a.nist.gov server time-b.nist.gov server time.nist.gov server time.windows.com server 0.pool.ntp.org server 1.pool.ntp.org server 2.pool.ntp.org server pool.ntp.org server 127.127.1.0 # local clock # ntpq -p remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter ============================================================================== +time-a.nist.gov .ACTS. 1 u 61 128 377 76.113 -1.046 3.424 *time-b.nist.gov .ACTS. 1 u 65 128 377 81.063 0.398 1.892 -time.nist.gov .ACTS. 1 u 251 128 356 38.911 1.353 30.226 -time.windows.co 18.26.4.105 2 u 45 128 267 31.218 13.180 6.039 -194.109.64.200 192.87.106.2 2 u 122 128 377 155.132 0.596 38.674 -a.mirror.fizzel 43.75.42.44 3 u 56 128 377 163.391 -11.756 13.006 -enfield.ikk.szt 195.111.99.186 2 u 118 128 377 188.326 -2.520 32.359 +ntp1.esat.net .GPS. 1 u 59 128 377 161.103 -1.321 0.460 LOCAL(0) .LOCL. 10 l 48 64 377 0.000 0.000 0.001
iptables -I INPUT -p udp -m udp --sport 123 -j ACCEPT
时间服务器作用:
大数据产生与处理系统是各种计算设备集群的,计算设备将统一、同步的标准时间用于记录各种事件发生时序,
如E-MAIL信息、文件创建和访问时间、数据库处理时间等。
大数据系统内不同计算设备之间控制、计算、处理、应用等数据或操作都具有时序性,
若计算机时间不同步,这些应用或操作或将无法正常进行。
大数据系统是对时间敏感的计算处理系统,时间同步是大数据能够得到正确处理的基础保障,是大数据得以发挥作用的技术支撑。
大数据时代,整个处理计算系统内的大数据通信都是通过网络进行。
时间同步也是如此,利用大数据的互联网络传送标准时间信息,实现大数据系统内时间同步。
网络时间同步协议(NTP)是时间同步的技术基础。
(一)确认ntp的安装
1)确认是否已安装ntp
【命令】rpm –qa | grep ntp
若只有ntpdate而未见ntp,则需删除原有ntpdate。如:
ntpdate-4.2.6p5-22.el7_0.x86_64
fontpackages-filesystem-1.44-8.el7.noarch
python-ntplib-0.3.2-1.el7.noarch
2)删除已安装ntp
【命令】yum –y remove ntpdate-4.2.6p5-22.el7.x86_64
3)重新安装ntp
【命令】yum –y install ntp
(二)配置ntp服务
1)修改所有节点的/etc/ntp.conf
【命令】vi /etc/ntp.conf
【内容】
restrict 192.168.6.3 nomodify notrap nopeer noquery //当前节点IP地址
restrict 192.168.6.2 mask 255.255.255.0 nomodify notrap //集群所在网段的网关(Gateway),子网掩码(Genmask)
2)选择一个主节点,修改其/etc/ntp.conf
【命令】vi /etc/ntp.conf
【内容】在server部分添加一下部分,并注释掉server 0 ~ n
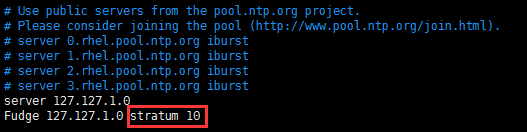
server 127.127.1.0
Fudge 127.127.1.0 stratum 10
3)主节点以外,继续修改/etc/ntp.conf
【命令】vi /etc/ntp.conf
【内容】在server部分添加如下语句,将server指向主节点。
server 192.168.6.3
Fudge 192.168.6.3 stratum 10
===修改前===
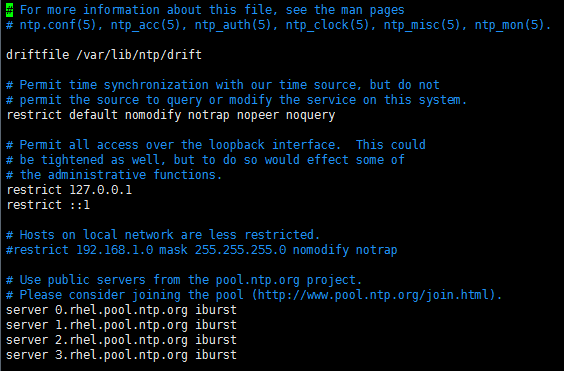
===修改后===
节点1(192.168.6.3):
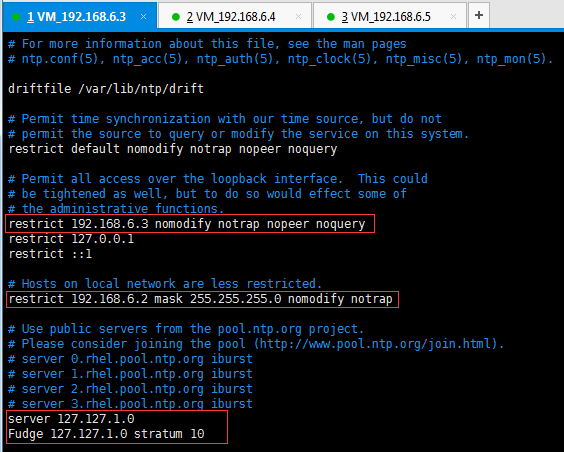
节点2(192.168.6.4):
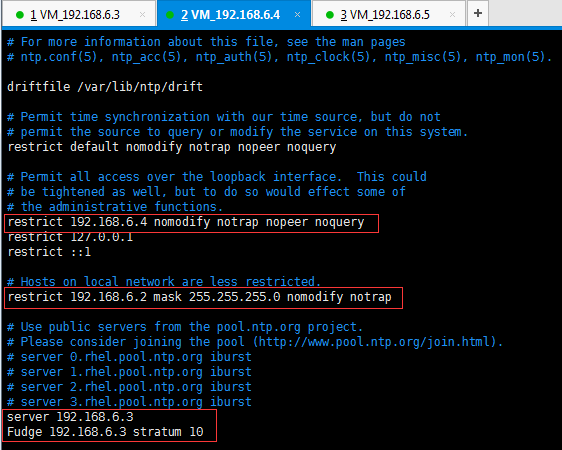
节点3(192.168.6.5):
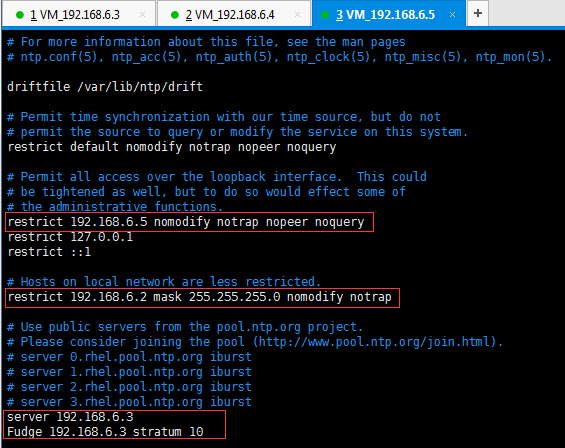
(三)启动ntp服务、查看状态
1)启动ntp服务
【命令】service ntpd start
2)查看ntp服务器有无和上层ntp连通
【命令】ntpstat
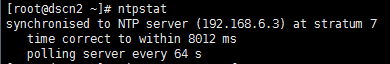
查看ntp状态时,可能会出现如下所示情况
① unsynchronised time server re-starting polling server every 8 s
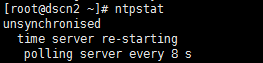
② unsynchronised polling server every 8 s
这种情况属于正常,ntp服务器配置完毕后,需要等待5-10分钟才能与/etc/ntp.conf中配置的标准时间进行同步。
等一段时间之后,再次使用ntpstat命令查看状态,就会变成如下正常结果:
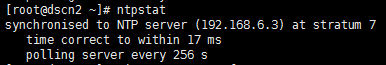
3)查看ntp服务器与上层ntp的状态
【命令】ntpq -p

remote:本机和上层ntp的ip或主机名,“+”表示优先,“*”表示次优先
refid:参考上一层ntp主机地址
st:stratum阶层
when:多少秒前曾经同步过时间
poll:下次更新在多少秒后
reach:已经向上层ntp服务器要求更新的次数
delay:网络延迟
offset:时间补偿
jitter:系统时间与bios时间差
4)查看ntpd进程的状态
【命令】watch "ntpq -p"
【终止】按 Ctrl+C 停止查看进程。
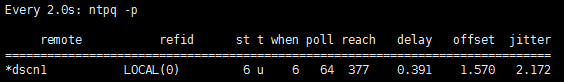
第一列中的字符指示源的质量。星号 ( * ) 表示该源是当前引用。
remote:列出源的 IP 地址或主机名。
when:指出从轮询源开始已过去的时间(秒)。
poll:指出轮询间隔时间。该值会根据本地时钟的精度相应增加。
reach:是一个八进制数字,指出源的可存取性。值 377 表示源已应答了前八个连续轮询。
offset:是源时钟与本地时钟的时间差(毫秒)。
(四)设置开机启动
【命令】chkconfig ntpd on
(五)从其他博客的一些参考摘录
===/etc/ntp.conf 配置内容===
# 1. 先处理权限方面的问题,包括放行上层服务器以及开放局域网用户来源: restrict default kod nomodify notrap nopeer noquery <==拒绝 IPv4 的用户 restrict -6 default kod nomodify notrap nopeer noquery <==拒绝 IPv6 的用户 restrict 220.130.158.71 <==放行 tock.stdtime.gov.tw 进入本 NTP 的服务器 restrict 59.124.196.83 <==放行 tick.stdtime.gov.tw 进入本 NTP 的服务器 restrict 59.124.196.84 <==放行 time.stdtime.gov.tw 进入本 NTP 的服务器 restrict 127.0.0.1 <==底下两个是默认值,放行本机来源 restrict -6 ::1restrict 192.168.100.0 mask 255.255.255.0 nomodify <==放行局域网用户来源,或者列出单独IP # 2. 设定主机来源,请先将原本的 [0|1|2].centos.pool.ntp.org 的设定批注掉: server 220.130.158.71 prefer <==以这部主机为最优先的server server 59.124.196.83server 59.124.196.84# 3.默认的一个内部时钟数据,用在没有外部 NTP 服务器时,使用它为局域网用户提供服务: # server 127.127.1.0 # local clock # fudge 127.127.1.0 stratum 10# 4.预设时间差异分析档案与暂不用到的 keys 等,不需要更动它: driftfile /var/lib/ntp/drift keys /etc/ntp/keys
===restrict选项格式===
restrict [ 客户端IP ] mask [ IP掩码 ] [参数]
“客户端IP” 和 “IP掩码” 指定了对网络中哪些范围的计算机进行控制,如果使用default关键字,则表示对所有的计算机进行控制,参数指定了具体的限制内容,常见的参数如下:
◆ ignore:拒绝连接到NTP服务器
◆ nomodiy: 客户端不能更改服务端的时间参数,但是客户端可以通过服务端进行网络校时。
◆ noquery: 不提供客户端的时间查询
◆ notrap: 不提供trap远程登录功能,trap服务是一种远程时间日志服务。
◆ notrust: 客户端除非通过认证,否则该客户端来源将被视为不信任子网 。
◆ nopeer: 提供时间服务,但不作为对等体。
◆ kod: 向不安全的访问者发送Kiss-Of-Death报文。
===server选项格式===
server host [ key n ] [ version n ] [ prefer ] [ mode n ] [ minpoll n ] [ maxpoll n ] [ iburst ]
其中host是上层NTP服务器的IP地址或域名,随后所跟的参数解释如下所示:
◆ key: 表示所有发往服务器的报文包含有秘钥加密的认证信息,n是32位的整数,表示秘钥号。
◆ version: 表示发往上层服务器的报文使用的版本号,n默认是3,可以是1或者2。
◆ prefer: 如果有多个server选项,具有该参数的服务器有限使用。
◆ mode: 指定数据报文mode字段的值。
◆ minpoll: 指定与查询该服务器的最小时间间隔为2的n次方秒,n默认为6,范围为4-14。
◆ maxpoll: 指定与查询该服务器的最大时间间隔为2的n次方秒,n默认为10,范围为4-14。
◆ iburst: 当初始同步请求时,采用突发方式接连发送8个报文,时间间隔为2秒。
===查看网关方法===
【命令1】route -n
【命令2】ip route show
【命令3】netstat -r
===层次(stratum)===
stratum根据上层server的层次而设定(+1)。
对于提供network time service provider的主机来说,stratum的设定要尽可能准确。
而作为局域网的time service provider,通常将stratum设置为10
0层的服务器采用的是原子钟、GPS钟等物理设备,stratum 1与stratum 0 是直接相连的,
往后的stratum与上一层stratum通过网络相连,同一层的server也可以交互。
ntpd对下层client来说是service server,对于上层server来说它是client。
ntpd根据配置文件的参数决定是要为其他服务器提供时钟服务或者是从其他服务器同步时钟。所有的配置都在/etc/ntp.conf文件中。






 微信支付宝扫一扫,打赏作者吧~
微信支付宝扫一扫,打赏作者吧~