ProcessHacker这款开源软件如官方所说是一款免费、强大的多用途工具,可帮助您监控系统资源、调试软件和检测恶意软件,我们可以通过学习其源代码在我们的软件中定时采集每个进程的CPU使用率、IO使用率等等,还有整机总的CPU使用率、GPU使用率、内存、磁盘使用情况等,具体可以参考ProcessHacker官网的介绍:Process Hacker Overview。最近在看进程CPU采集的代码,参考的是processhacker的源代码的采集逻辑,processhacker是每隔1秒钟采集一次当前进程的CPU使用率的,当然我们也可以根据自己需要将进程的CPU采集频率改小一些,或者改大一些。于是尝试使用VS2022打开processhacker源代码编译运行,看一下进程CPU使用率的采集流程,当然ProcessHacker除了可以采集进程的CPU使用率之外,还可以进程的采集IO使用率等。
一、ProcessHacker源代码下载
我使用的processhacker源代码下载地址为:https://github.com/PKRoma/ProcessHacker
processhacker官方的地址为:https://repology.org/project/processhacker/information
sourceforge.net地址为:https://sourceforge.net/projects/processhacker/
二、安装VS2022
这一步要注意,安装VS2022时把与VC++相关的组件选上,具体安装步骤就不详述了。
三、使用VS2022编译运行ProcessHacker源代码
使用VS2022打开第1步的[https://github.com/PKRoma/ProcessHacker](https://github.com/PKRoma/ProcessHacker)源代码,然后编译运行,如下图所示:
如果像上面一样,说明在VS2022中编译ProcessHacker源代码成功了。
接下来我们运行看一下,
可以先忽略上面的一些dll加载失败的情况,点击【确定】接着运行,
4.调试运行ProcessHacker,看看进程CPU采集逻辑
接下来我们可以看看ProcessHacker中关于进程CPU采集逻辑的代码,具体目录为:ProcessHacker-master\ProcessHacker\procprv.c,procprv.c在线源代码文件地址为:https://processhacker.sourceforge.io/doc/procprv_8c_source.html
procprv.c File Reference 如下图所示:
(1) main.c: PhMainWndInitialization
if (!PhMainWndInitialization(CmdShow))
{
PhShowError(NULL, L"%s", L"Unable to initialize the main window.");
return 1;
}(2) mainwnd.c: PhRegisterProvider
PhRegisterProvider(&PhPrimaryProviderThread, PhProcessProviderUpdate, NULL, &PhMwpProcessProviderRegistration);
(3)procprv.c: PhProcessProviderUpdate,这个是进程CPU采集的核心函数
VOID PhProcessProviderUpdate(
_In_ PVOID Object
){
static ULONG runCount = 0;
static PSYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION pidBuckets[PROCESS_ID_BUCKETS];
// Note about locking:
//
// Since this is the only function that is allowed to modify the process hashtable, locking is
// not needed for shared accesses. However, exclusive accesses need locking.
PVOID processes;
PSYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION process;
ULONG bucketIndex;
ULONG64 sysTotalTime; // total time for this update period
ULONG64 sysTotalCycleTime = 0; // total cycle time for this update period
ULONG64 sysIdleCycleTime = 0; // total idle cycle time for this update period
FLOAT maxCpuValue = 0;
PPH_PROCESS_ITEM maxCpuProcessItem = NULL;
ULONG64 maxIoValue = 0;
PPH_PROCESS_ITEM maxIoProcessItem = NULL;
// Pre-update tasks
if (runCount % 512 == 0) // yes, a very long time
{
if (PhEnablePurgeProcessRecords)
PhPurgeProcessRecords();
PhpFlushSidFullNameCache();
PhImageListFlushCache();
PhFlushImageVersionInfoCache();
//PhFlushVerifyCache();
}
if (!PhProcessStatisticsInitialized)
{
PhpInitializeProcessStatistics();
PhProcessStatisticsInitialized = TRUE;
}
PhpUpdatePerfInformation();
if (PhEnableCycleCpuUsage)
{
PhpUpdateCpuInformation(FALSE, &sysTotalTime);
PhpUpdateCpuCycleInformation(&sysIdleCycleTime);
}
else
{
PhpUpdateCpuInformation(TRUE, &sysTotalTime);
}
if (runCount != 0)
{
PhTimeSequenceNumber++;
}
// Get the process list.
PhTotalProcesses = 0;
PhTotalThreads = 0;
PhTotalHandles = 0;
PhTotalCpuQueueLength = 0;
if (!NT_SUCCESS(PhEnumProcesses(&processes)))
return;
// Notes on cycle-based CPU usage:
//
// Cycle-based CPU usage is a bit tricky to calculate because we cannot get the total number of
// cycles consumed by all processes since system startup - we can only get total number of
// cycles per process. This means there are two ways to calculate the system-wide cycle time
// delta:
//
// 1. Each update, sum the cycle times of all processes, and calculate the system-wide delta
// from this. Process Explorer seems to do this.
// 2. Each update, calculate the cycle time delta for each individual process, and sum these
// deltas to create the system-wide delta. We use this here.
//
// The first method is simpler but has a problem when a process exits and its cycle time is no
// longer counted in the system-wide total. This may cause the delta to be negative and all
// other calculations to become invalid. Process Explorer simply ignored this fact and treated
// the system-wide delta as unsigned (and therefore huge when negative), leading to all CPU
// usages being displayed as "< 0.01".
//
// The second method is used here, but the adjustments must be done before the main new/modified
// pass. We need take into account new, existing and terminated processes.
// Create the PID hash set. This contains the process information structures returned by
// PhEnumProcesses, distinct from the process item hash set. Note that we use the
// UniqueProcessKey field as the next node pointer to avoid having to allocate extra memory.
memset(pidBuckets, 0, sizeof(pidBuckets));
process = PH_FIRST_PROCESS(processes);
do
{
PhTotalProcesses++;
PhTotalThreads += process->NumberOfThreads;
PhTotalHandles += process->HandleCount;
if (process->UniqueProcessId == SYSTEM_IDLE_PROCESS_ID)
{
process->CycleTime = PhCpuIdleCycleDelta.Value;
process->KernelTime = PhCpuTotals.IdleTime;
}
bucketIndex = PROCESS_ID_TO_BUCKET_INDEX(process->UniqueProcessId);
process->UniqueProcessKey = (ULONG_PTR)pidBuckets[bucketIndex];
pidBuckets[bucketIndex] = process;
if (PhEnableCycleCpuUsage)
{
PPH_PROCESS_ITEM processItem;
if (PhEnableProcessExtension)
{
if ((processItem = PhpLookupProcessItem(process->UniqueProcessId)) && processItem->ProcessSequenceNumber == PH_PROCESS_EXTENSION(process)->ProcessSequenceNumber)
sysTotalCycleTime += process->CycleTime - processItem->CycleTimeDelta.Value; // existing process
else
sysTotalCycleTime += process->CycleTime; // new process
}
else
{
if ((processItem = PhpLookupProcessItem(process->UniqueProcessId)) && processItem->CreateTime.QuadPart == process->CreateTime.QuadPart)
sysTotalCycleTime += process->CycleTime - processItem->CycleTimeDelta.Value; // existing process
else
sysTotalCycleTime += process->CycleTime; // new process
}
}
} while (process = PH_NEXT_PROCESS(process));
// Add the fake processes to the PID list.
//
// On Windows 7 the two fake processes are merged into "Interrupts" since we can only get cycle
// time information both DPCs and Interrupts combined.
if (PhEnableCycleCpuUsage)
{
PhInterruptsProcessInformation->KernelTime.QuadPart = PhCpuTotals.DpcTime.QuadPart + PhCpuTotals.InterruptTime.QuadPart;
PhInterruptsProcessInformation->CycleTime = PhCpuSystemCycleDelta.Value;
sysTotalCycleTime += PhCpuSystemCycleDelta.Delta;
}
else
{
PhDpcsProcessInformation->KernelTime = PhCpuTotals.DpcTime;
PhInterruptsProcessInformation->KernelTime = PhCpuTotals.InterruptTime;
}
// Look for dead processes.
{
PPH_LIST processesToRemove = NULL;
ULONG i;
PPH_HASH_ENTRY entry;
PPH_PROCESS_ITEM processItem;
PSYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION processEntry;
for (i = 0; i < PH_HASH_SET_SIZE(PhProcessHashSet); i++)
{
for (entry = PhProcessHashSet[i]; entry; entry = entry->Next)
{
BOOLEAN processRemoved = FALSE;
processItem = CONTAINING_RECORD(entry, PH_PROCESS_ITEM, HashEntry);
// Check if the process still exists. Note that we take into account PID re-use by
// checking CreateTime as well.
if (processItem->ProcessId == DPCS_PROCESS_ID)
{
processEntry = PhDpcsProcessInformation;
}
else if (processItem->ProcessId == INTERRUPTS_PROCESS_ID)
{
processEntry = PhInterruptsProcessInformation;
}
else
{
processEntry = pidBuckets[PROCESS_ID_TO_BUCKET_INDEX(processItem->ProcessId)];
while (processEntry && processEntry->UniqueProcessId != processItem->ProcessId)
processEntry = (PSYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION)processEntry->UniqueProcessKey;
}
if (PhEnableProcessExtension)
{
if (!processEntry || PH_PROCESS_EXTENSION(processEntry)->ProcessSequenceNumber != processItem->ProcessSequenceNumber)
processRemoved = TRUE;
}
else
{
if (!processEntry || processEntry->CreateTime.QuadPart != processItem->CreateTime.QuadPart)
processRemoved = TRUE;
}
if (processRemoved)
{
LARGE_INTEGER exitTime;
processItem->State |= PH_PROCESS_ITEM_REMOVED;
exitTime.QuadPart = 0;
if (processItem->QueryHandle)
{
KERNEL_USER_TIMES times;
ULONG64 finalCycleTime;
if (NT_SUCCESS(PhGetProcessTimes(processItem->QueryHandle, ×)))
{
exitTime = times.ExitTime;
}
if (PhEnableCycleCpuUsage)
{
if (NT_SUCCESS(PhGetProcessCycleTime(processItem->QueryHandle, &finalCycleTime)))
{
// Adjust deltas for the terminated process because this doesn't get
// picked up anywhere else.
//
// Note that if we don't have sufficient access to the process, the
// worst that will happen is that the CPU usages of other processes
// will get inflated. (See above; if we were using the first
// technique, we could get negative deltas, which is much worse.)
sysTotalCycleTime += finalCycleTime - processItem->CycleTimeDelta.Value;
}
}
}
// If we don't have a valid exit time, use the current time.
if (exitTime.QuadPart == 0)
PhQuerySystemTime(&exitTime);
processItem->Record->Flags |= PH_PROCESS_RECORD_DEAD;
processItem->Record->ExitTime = exitTime;
// Raise the process removed event.
PhInvokeCallback(PhGetGeneralCallback(GeneralCallbackProcessProviderRemovedEvent), processItem);
if (!processesToRemove)
processesToRemove = PhCreateList(2);
PhAddItemList(processesToRemove, processItem);
}
}
}
// Lock only if we have something to do.
if (processesToRemove)
{
PhAcquireQueuedLockExclusive(&PhProcessHashSetLock);
for (i = 0; i < processesToRemove->Count; i++)
{
PhpRemoveProcessItem((PPH_PROCESS_ITEM)processesToRemove->Items[i]);
}
PhReleaseQueuedLockExclusive(&PhProcessHashSetLock);
PhDereferenceObject(processesToRemove);
}
}
// Go through the queued process query data.
PhFlushProcessQueryData();
if (sysTotalTime == 0)
sysTotalTime = -1; // max. value
if (sysTotalCycleTime == 0)
sysTotalCycleTime = -1;
PhCpuTotalCycleDelta = sysTotalCycleTime;
// Look for new processes and update existing ones.
process = PH_FIRST_PROCESS(processes);
while (process)
{
PPH_PROCESS_ITEM processItem;
processItem = PhpLookupProcessItem(process->UniqueProcessId);
if (!processItem)
{
PPH_PROCESS_RECORD processRecord;
BOOLEAN isSuspended;
BOOLEAN isPartiallySuspended;
ULONG64 contextSwitches;
ULONG processorQueueLength;
// Create the process item and fill in basic information.
processItem = PhCreateProcessItem(process->UniqueProcessId);
PhpFillProcessItem(processItem, process);
PhpFillProcessItemExtension(processItem, process);
processItem->TimeSequenceNumber = PhTimeSequenceNumber;
processRecord = PhpCreateProcessRecord(processItem);
PhpAddProcessRecord(processRecord);
processItem->Record = processRecord;
PhpGetProcessThreadInformation(process, &isSuspended, &isPartiallySuspended, &contextSwitches, &processorQueueLength);
PhpUpdateDynamicInfoProcessItem(processItem, process);
PhTotalCpuQueueLength += processorQueueLength;
// Initialize the deltas.
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->CpuKernelDelta, process->KernelTime.QuadPart);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->CpuUserDelta, process->UserTime.QuadPart);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->IoReadDelta, process->ReadTransferCount.QuadPart);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->IoWriteDelta, process->WriteTransferCount.QuadPart);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->IoOtherDelta, process->OtherTransferCount.QuadPart);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->IoReadCountDelta, process->ReadOperationCount.QuadPart);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->IoWriteCountDelta, process->WriteOperationCount.QuadPart);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->IoOtherCountDelta, process->OtherOperationCount.QuadPart);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->ContextSwitchesDelta, PhEnableProcessExtension ? processItem->ContextSwitches : contextSwitches);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->PageFaultsDelta, process->PageFaultCount);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->HardFaultsDelta, process->HardFaultCount);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->CycleTimeDelta, process->CycleTime);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->PrivateBytesDelta, process->PagefileUsage);
processItem->IsSuspended = isSuspended;
processItem->IsPartiallySuspended = isPartiallySuspended;
// If this is the first run of the provider, queue the
// process query tasks. Otherwise, perform stage 1
// processing now and queue stage 2 processing.
if (runCount > 0)
{
PH_PROCESS_QUERY_S1_DATA data;
memset(&data, 0, sizeof(PH_PROCESS_QUERY_S1_DATA));
data.Header.Stage = 1;
data.Header.ProcessItem = processItem;
PhpProcessQueryStage1(&data);
PhpFillProcessItemStage1(&data);
PhSetEvent(&processItem->Stage1Event);
}
else
{
PhpQueueProcessQueryStage1(processItem);
}
// Add pending service items to the process item.
PhUpdateProcessItemServices(processItem);
// Add the process item to the hashtable.
PhAcquireQueuedLockExclusive(&PhProcessHashSetLock);
PhpAddProcessItem(processItem);
PhReleaseQueuedLockExclusive(&PhProcessHashSetLock);
// Raise the process added event.
PhInvokeCallback(PhGetGeneralCallback(GeneralCallbackProcessProviderAddedEvent), processItem);
// (Ref: for the process item being in the hashtable.)
// Instead of referencing then dereferencing we simply don't do anything.
// Dereferenced in PhpRemoveProcessItem.
}
else
{
BOOLEAN modified = FALSE;
BOOLEAN isSuspended;
BOOLEAN isPartiallySuspended;
ULONG64 contextSwitches;
ULONG readyThreads;
FLOAT newCpuUsage;
FLOAT kernelCpuUsage;
FLOAT userCpuUsage;
PhpGetProcessThreadInformation(process, &isSuspended, &isPartiallySuspended, &contextSwitches, &readyThreads);
PhpUpdateDynamicInfoProcessItem(processItem, process);
PhpFillProcessItemExtension(processItem, process);
PhTotalCpuQueueLength += readyThreads;
// Update the deltas.
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->CpuKernelDelta, process->KernelTime.QuadPart);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->CpuUserDelta, process->UserTime.QuadPart);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->IoReadDelta, process->ReadTransferCount.QuadPart);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->IoWriteDelta, process->WriteTransferCount.QuadPart);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->IoOtherDelta, process->OtherTransferCount.QuadPart);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->IoReadCountDelta, process->ReadOperationCount.QuadPart);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->IoWriteCountDelta, process->WriteOperationCount.QuadPart);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->IoOtherCountDelta, process->OtherOperationCount.QuadPart);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->ContextSwitchesDelta, PhEnableProcessExtension ? processItem->ContextSwitches : contextSwitches);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->PageFaultsDelta, process->PageFaultCount);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->HardFaultsDelta, process->HardFaultCount);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->CycleTimeDelta, process->CycleTime);
PhUpdateDelta(&processItem->PrivateBytesDelta, process->PagefileUsage);
processItem->TimeSequenceNumber++;
PhAddItemCircularBuffer_ULONG64(&processItem->IoReadHistory, processItem->IoReadDelta.Delta);
PhAddItemCircularBuffer_ULONG64(&processItem->IoWriteHistory, processItem->IoWriteDelta.Delta);
PhAddItemCircularBuffer_ULONG64(&processItem->IoOtherHistory, processItem->IoOtherDelta.Delta);
PhAddItemCircularBuffer_SIZE_T(&processItem->PrivateBytesHistory, processItem->VmCounters.PagefileUsage);
//PhAddItemCircularBuffer_SIZE_T(&processItem->WorkingSetHistory, processItem->VmCounters.WorkingSetSize);
if (InterlockedExchange(&processItem->JustProcessed, 0) != 0)
modified = TRUE;
if (PhEnableCycleCpuUsage)
{
FLOAT totalDelta;
newCpuUsage = (FLOAT)processItem->CycleTimeDelta.Delta / sysTotalCycleTime;
// Calculate the kernel/user CPU usage based on the kernel/user time. If the kernel
// and user deltas are both zero, we'll just have to use an estimate. Currently, we
// split the CPU usage evenly across the kernel and user components, except when the
// total user time is zero, in which case we assign it all to the kernel component.
totalDelta = (FLOAT)(processItem->CpuKernelDelta.Delta + processItem->CpuUserDelta.Delta);
if (totalDelta != 0)
{
kernelCpuUsage = newCpuUsage * ((FLOAT)processItem->CpuKernelDelta.Delta / totalDelta);
userCpuUsage = newCpuUsage * ((FLOAT)processItem->CpuUserDelta.Delta / totalDelta);
}
else
{
if (processItem->UserTime.QuadPart != 0)
{
kernelCpuUsage = newCpuUsage / 2;
userCpuUsage = newCpuUsage / 2;
}
else
{
kernelCpuUsage = newCpuUsage;
userCpuUsage = 0;
}
}
}
else
{
kernelCpuUsage = (FLOAT)processItem->CpuKernelDelta.Delta / sysTotalTime;
userCpuUsage = (FLOAT)processItem->CpuUserDelta.Delta / sysTotalTime;
newCpuUsage = kernelCpuUsage + userCpuUsage;
}
processItem->CpuUsage = newCpuUsage;
processItem->CpuKernelUsage = kernelCpuUsage;
processItem->CpuUserUsage = userCpuUsage;
PhAddItemCircularBuffer_FLOAT(&processItem->CpuKernelHistory, kernelCpuUsage);
PhAddItemCircularBuffer_FLOAT(&processItem->CpuUserHistory, userCpuUsage);
// Max. values
if (processItem->ProcessId)
{
if (maxCpuValue < newCpuUsage)
{
maxCpuValue = newCpuUsage;
maxCpuProcessItem = processItem;
}
// I/O for Other is not included because it is too generic.
if (maxIoValue < processItem->IoReadDelta.Delta + processItem->IoWriteDelta.Delta)
{
maxIoValue = processItem->IoReadDelta.Delta + processItem->IoWriteDelta.Delta;
maxIoProcessItem = processItem;
}
}
// Token information
if (
processItem->QueryHandle &&
processItem->ProcessId != SYSTEM_PROCESS_ID // System token can't be opened on XP (wj32)
)
{
HANDLE tokenHandle;
if (NT_SUCCESS(PhOpenProcessToken(
processItem->QueryHandle,
TOKEN_QUERY,
&tokenHandle )))
{
PTOKEN_USER tokenUser;
TOKEN_ELEVATION_TYPE elevationType;
MANDATORY_LEVEL integrityLevel;
PWSTR integrityString;
// User
if (NT_SUCCESS(PhGetTokenUser(tokenHandle, &tokenUser)))
{
if (!processItem->Sid || !RtlEqualSid(processItem->Sid, tokenUser->User.Sid))
{
PSID processSid;
// HACK (dmex)
processSid = processItem->Sid;
processItem->Sid = PhAllocateCopy(tokenUser->User.Sid, RtlLengthSid(tokenUser->User.Sid));
if (processSid) PhFree(processSid);
PhMoveReference(&processItem->UserName, PhpGetSidFullNameCachedSlow(processItem->Sid));
modified = TRUE;
}
PhFree(tokenUser);
}
// Elevation
if (NT_SUCCESS(PhGetTokenElevationType(tokenHandle, &elevationType)))
{
if (processItem->ElevationType != elevationType)
{
processItem->ElevationType = elevationType;
processItem->IsElevated = elevationType == TokenElevationTypeFull;
modified = TRUE;
}
}
// Integrity
if (NT_SUCCESS(PhGetTokenIntegrityLevel(tokenHandle, &integrityLevel, &integrityString)))
{
if (processItem->IntegrityLevel != integrityLevel)
{
processItem->IntegrityLevel = integrityLevel;
processItem->IntegrityString = integrityString;
modified = TRUE;
}
}
NtClose(tokenHandle);
}
}
// Job
if (processItem->QueryHandle)
{
NTSTATUS status;
BOOLEAN isInSignificantJob = FALSE;
BOOLEAN isInJob = FALSE;
if (KphIsConnected())
{
HANDLE jobHandle = NULL;
status = KphOpenProcessJob(
processItem->QueryHandle,
JOB_OBJECT_QUERY,
&jobHandle );
if (NT_SUCCESS(status) && status != STATUS_PROCESS_NOT_IN_JOB)
{
JOBOBJECT_BASIC_LIMIT_INFORMATION basicLimits;
isInJob = TRUE;
if (NT_SUCCESS(PhGetJobBasicLimits(jobHandle, &basicLimits)))
{
isInSignificantJob = basicLimits.LimitFlags != JOB_OBJECT_LIMIT_SILENT_BREAKAWAY_OK;
}
}
if (jobHandle)
NtClose(jobHandle);
}
else
{
status = NtIsProcessInJob(processItem->QueryHandle, NULL);
if (NT_SUCCESS(status))
isInJob = status == STATUS_PROCESS_IN_JOB;
}
if (processItem->IsInSignificantJob != isInSignificantJob)
{
processItem->IsInSignificantJob = isInSignificantJob;
modified = TRUE;
}
if (processItem->IsInJob != isInJob)
{
processItem->IsInJob = isInJob;
modified = TRUE;
}
}
// Debugged
if (
processItem->QueryHandle &&
!processItem->IsSubsystemProcess &&
!processItem->IsProtectedHandle && // Don't query the debug object if the handle was filtered (dmex)
processItem->ProcessId != SYSTEM_PROCESS_ID // Ignore the system process on 20H2 (dmex)
)
{
BOOLEAN isBeingDebugged = FALSE;
PhGetProcessIsBeingDebugged(processItem->QueryHandle, &isBeingDebugged);
if (processItem->IsBeingDebugged != isBeingDebugged)
{
processItem->IsBeingDebugged = isBeingDebugged;
modified = TRUE;
}
}
// Suspended
if (processItem->IsSuspended != isSuspended)
{
processItem->IsSuspended = isSuspended;
modified = TRUE;
}
if (PhCsUseColorPartiallySuspended) // HACK // Don't invalidate for partially suspended unless enabled (dmex)
{
if (processItem->IsPartiallySuspended != isPartiallySuspended)
{
processItem->IsPartiallySuspended = isPartiallySuspended;
modified = TRUE;
}
}
else
{
processItem->IsPartiallySuspended = isPartiallySuspended;
}
// .NET
if (processItem->UpdateIsDotNet)
{
BOOLEAN isDotNet;
ULONG flags = 0;
if (NT_SUCCESS(PhGetProcessIsDotNetEx(processItem->ProcessId, NULL, 0, &isDotNet, &flags)))
{
processItem->IsDotNet = isDotNet;
modified = TRUE;
}
processItem->UpdateIsDotNet = FALSE;
}
// Immersive
if (processItem->QueryHandle && WindowsVersion >= WINDOWS_8 && !processItem->IsSubsystemProcess)
{
BOOLEAN isImmersive;
isImmersive = PhIsImmersiveProcess(processItem->QueryHandle);
if (processItem->IsImmersive != isImmersive)
{
processItem->IsImmersive = isImmersive;
modified = TRUE;
}
}
if (processItem->QueryHandle && processItem->IsHandleValid)
{
OBJECT_BASIC_INFORMATION basicInfo;
BOOLEAN filteredHandle = FALSE;
if (NT_SUCCESS(PhGetHandleInformationEx(
NtCurrentProcess(),
processItem->QueryHandle,
ULONG_MAX,
0,
NULL,
&basicInfo,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL
)))
{
if (!RtlAreAllAccessesGranted(basicInfo.GrantedAccess, PROCESS_QUERY_INFORMATION))
{
filteredHandle = TRUE;
}
}
else
{
filteredHandle = TRUE;
}
if (processItem->IsProtectedHandle != filteredHandle)
{
processItem->IsProtectedHandle = filteredHandle;
modified = TRUE;
}
}
if (modified)
{
PhInvokeCallback(PhGetGeneralCallback(GeneralCallbackProcessProviderModifiedEvent), processItem);
}
// No reference added by PhpLookupProcessItem.
}
// Trick ourselves into thinking that the fake processes
// are on the list.
if (process == PhInterruptsProcessInformation)
{
process = NULL;
}
else if (process == PhDpcsProcessInformation)
{
process = PhInterruptsProcessInformation;
}
else
{
process = PH_NEXT_PROCESS(process);
if (process == NULL)
{
if (PhEnableCycleCpuUsage)
process = PhInterruptsProcessInformation;
else
process = PhDpcsProcessInformation;
}
}
}
if (PhProcessInformation)
PhFree(PhProcessInformation);
PhProcessInformation = processes;
// History cannot be updated on the first run because the deltas are invalid. For example, the
// I/O "deltas" will be huge because they are currently the raw accumulated values.
if (runCount != 0)
{
if (PhEnableCycleCpuUsage)
PhpUpdateCpuCycleUsageInformation(sysTotalCycleTime, sysIdleCycleTime);
PhpUpdateSystemHistory();
// Note that we need to add a reference to the records of these processes, to make it
// possible for others to get the name of a max. CPU or I/O process.
if (maxCpuProcessItem)
{
PhAddItemCircularBuffer_ULONG(&PhMaxCpuHistory, HandleToUlong(maxCpuProcessItem->ProcessId));#ifdef PH_RECORD_MAX_USAGE
PhAddItemCircularBuffer_FLOAT(&PhMaxCpuUsageHistory, maxCpuProcessItem->CpuUsage);#endif if (!(maxCpuProcessItem->Record->Flags & PH_PROCESS_RECORD_STAT_REF))
{
PhReferenceProcessRecord(maxCpuProcessItem->Record);
maxCpuProcessItem->Record->Flags |= PH_PROCESS_RECORD_STAT_REF;
}
}
else
{
PhAddItemCircularBuffer_ULONG(&PhMaxCpuHistory, PtrToUlong(NULL));#ifdef PH_RECORD_MAX_USAGE
PhAddItemCircularBuffer_FLOAT(&PhMaxCpuUsageHistory, 0);#endif }
if (maxIoProcessItem)
{
PhAddItemCircularBuffer_ULONG(&PhMaxIoHistory, HandleToUlong(maxIoProcessItem->ProcessId));#ifdef PH_RECORD_MAX_USAGE
PhAddItemCircularBuffer_ULONG64(&PhMaxIoReadOtherHistory,
maxIoProcessItem->IoReadDelta.Delta + maxIoProcessItem->IoOtherDelta.Delta);
PhAddItemCircularBuffer_ULONG64(&PhMaxIoWriteHistory, maxIoProcessItem->IoWriteDelta.Delta);#endif if (!(maxIoProcessItem->Record->Flags & PH_PROCESS_RECORD_STAT_REF))
{
PhReferenceProcessRecord(maxIoProcessItem->Record);
maxIoProcessItem->Record->Flags |= PH_PROCESS_RECORD_STAT_REF;
}
}
else
{
PhAddItemCircularBuffer_ULONG(&PhMaxIoHistory, PtrToUlong(NULL));#ifdef PH_RECORD_MAX_USAGE
PhAddItemCircularBuffer_ULONG64(&PhMaxIoReadOtherHistory, 0);
PhAddItemCircularBuffer_ULONG64(&PhMaxIoWriteHistory, 0);#endif }
}
PhInvokeCallback(PhGetGeneralCallback(GeneralCallbackProcessProviderUpdatedEvent), NULL);
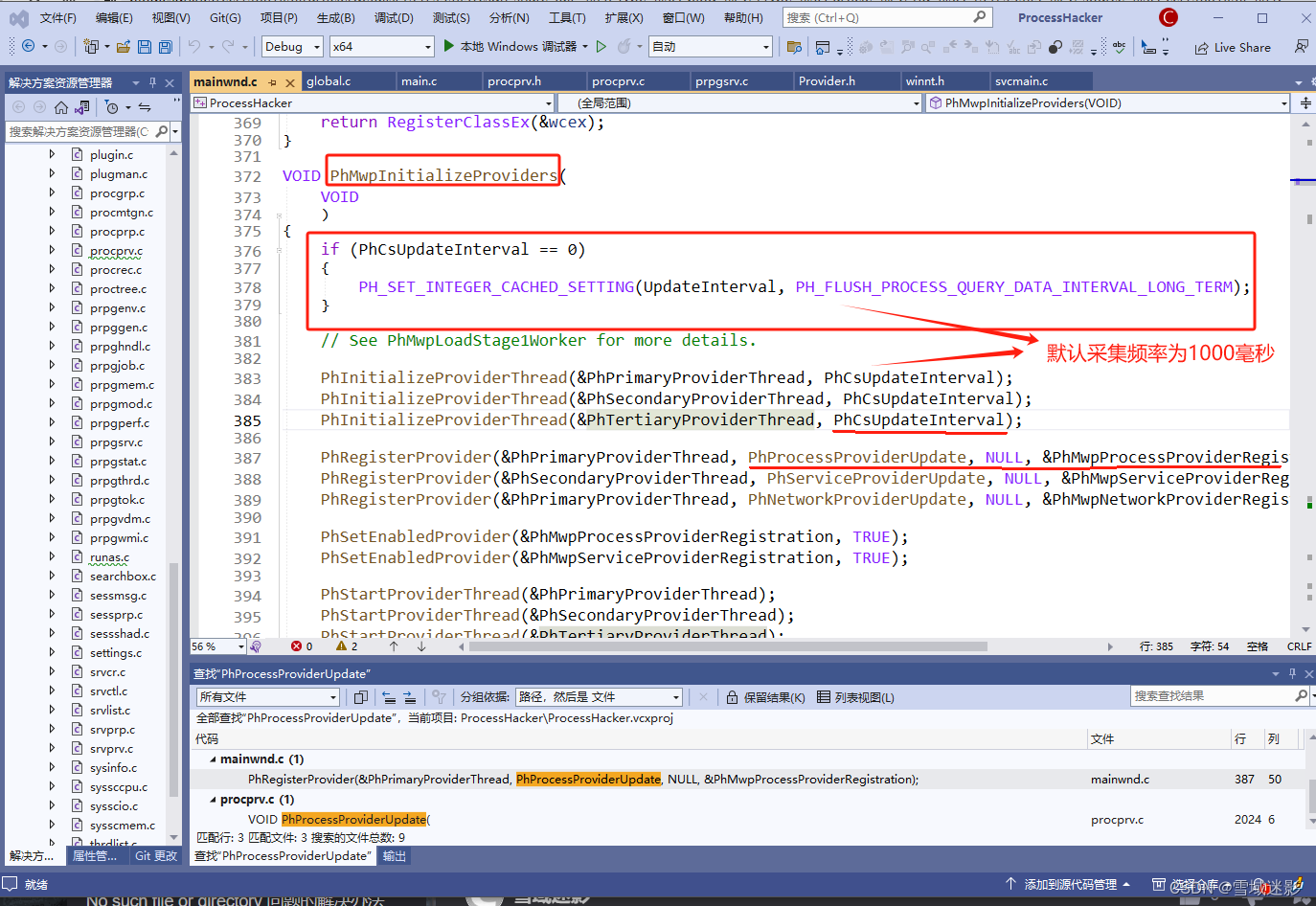
runCount++;}进程CPU采集频率可以查看mainwnd.c文件中的PhMwpInitializeProviders函数,PhCsUpdateInterval变量对应采集间隔,默认值为:1000:
#define PH_FLUSH_PROCESS_QUERY_DATA_INTERVAL_LONG_TERM 1000
四、参考资料
processhacker源代码下载地址为:https://github.com/PKRoma/ProcessHacker
推荐本站淘宝优惠价购买喜欢的宝贝:
本文链接:https://hqyman.cn/post/6993.html 非本站原创文章欢迎转载,原创文章需保留本站地址!
休息一下~~



 微信支付宝扫一扫,打赏作者吧~
微信支付宝扫一扫,打赏作者吧~