https://github.com/wangyu-/UDPping
ping with UDP protocol ?
root@raspberrypi:~# ./udpping.py 44.55.66.77 4000 UDPping 44.55.66.77 via port 4000 with 64 bytes of payload Reply from 44.55.66.77 seq=0 time=138.357 ms Reply from 44.55.66.77 seq=1 time=128.062 ms Request timed out Reply from 44.55.66.77 seq=3 time=136.370 ms Reply from 44.55.66.77 seq=4 time=140.743 ms Request timed out Reply from 44.55.66.77 seq=6 time=143.438 ms Reply from 44.55.66.77 seq=7 time=142.684 ms Reply from 44.55.66.77 seq=8 time=138.871 ms Reply from 44.55.66.77 seq=9 time=138.990 ms ^C --- ping statistics --- 10 packets transmitted, 8 received, 20.00% packet loss rtt min/avg/max = 128.06/138.44/143.44 ms
Set up a udp echo server at the host you want to ping.
There are many ways of doing this, my favourite way is:
socat -v UDP-LISTEN:4000,fork PIPE
Now a echo server is listening at port 4000.
If you dont have socat, use apt install socat or yum install socat, you will get it.
Ping you server.
Assume 44.55.66.77 is the IP of your server.
./udpping.py 44.55.66.77 4000
Done!
Now UDPping will generate outputs as a normal ping, but the protocol used is UDP instead of ICMP.
root@raspberrypi:~# ./udpping.py usage: this_program <dest_ip> <dest_port> this_program <dest_ip> <dest_port> "<options>" options: LEN the length of payload, unit:byte INTERVAL the seconds waited between sending each packet, as well as the timeout for reply packet, unit: ms examples: ./udpping.py 44.55.66.77 4000 ./udpping.py 44.55.66.77 4000 "LEN=400;INTERVAL=2000" ./udpping.py fe80::5400:ff:aabb:ccdd 4000
测试服务器的udping值
参考
步骤一:在服务器上启动`UDP Echo`服务(必须)
启动`UDP Echo服务`
步骤二:在客户端下载UDPing工具
步骤三:在客户端测试UDPing值
参考
https://help.aliyun.com/document_detail/158771.html
UDPing项目地址: https://github.com/wangyu-/UDPping
步骤一:在服务器上启动UDP Echo服务(必须)
要使用UDPing测试加速效果,终端节点服务器必须部署UDP Echo服务。本示例使用Socat模拟UDP服务端为例,介绍如何部署UDP Echo服务。
# 安装Socat
## Centos7
yum install socat -y
## ubuntu
apt install socat -y
## Windows下msys2安装
pacman -S socat
启动UDP Echo服务
# 在服务器上创建一个不间断会话(防止ssh断开推出)
screen -R udping
## -v 详细数据流量,文本
## -udp-listen:<port> 监听UDP端口
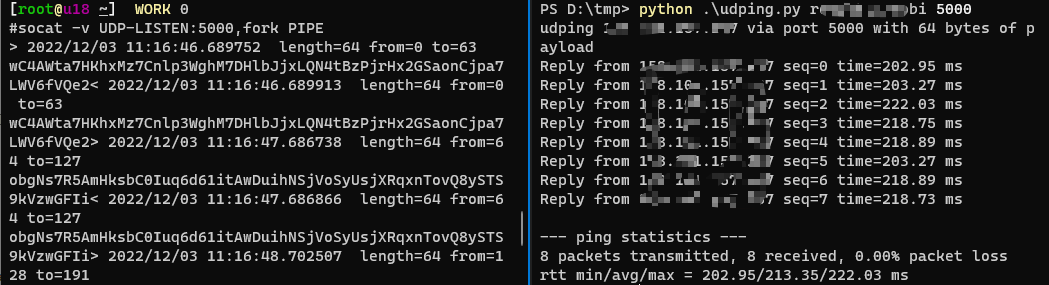
socat -v UDP-LISTEN:5000,fork PIPE
Widnows系统直接运行socat.exe的绝对路径,也可以成功运行socat。
步骤二:在客户端下载UDPing工具
完成以下操作,在客户端部署UDPing工具。(Windows和Linux均可,python2和python3均可)
项目地址: https://github.com/wangyu-/UDPping
执行以下命令,下载UDPing工具。
# 下载UDPing工具
wget -c https://networktools-public.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/ga/udping/udping.py
# 赋予UDPing工具执行权限。
chmod +x udping.py
步骤三:在客户端测试UDPing值
# python udping.py 服务端ip地址 UDP端口号
python .\udping.py 171.xxx.xxx.80 5000
————————————————
如果您的全球加速配置的监听协议是UDP协议,您可以通过UDPing测试全球加速的加速效果,UDPing使用特定的端口号将UDP ping发送到特定的IP地址。本文以终端节点服务器和客户端都为CentOS系统为例,介绍如何通过UDPing测试UDP监听协议的网络加速效果。
https://help.aliyun.com/zh/ga/use-cases/test-the-acceleration-performance-of-a-ga-instance-that-uses-a-udp-listener
前提条件
开始前,请确保满足以下条件。
您已经添加了监听,且监听协议为UDP协议。详细信息,请参见添加和管理智能路由类型监听。
您已经在终端节点服务器上将监听端口添加到安全配置(例如安全组)白名单中。
背景信息
全球加速采用四层(TCP/UDP协议)转发模式,无法使用ICMP Ping和TCPing测试UDP监听协议的加速效果,但您可以使用UDPing测试UDP监听协议的加速效果。
UDP是数据报机制,无会话连接,直接将UDP报文转发给终端节点组中的终端节点。
步骤一:在终端节点服务器上部署UDP Echo服务
要使用UDPing测试加速效果,终端节点服务器必须部署UDP Echo服务。本示例使用Socat模拟UDP服务端为例,介绍如何部署UDP Echo服务。
执行以下命令,安装Socat。
yum install socat执行以下命令,启动Socat。
nohup socat -v UDP-LISTEN:<监听端口>,fork PIPE 2>/dev/null &
步骤二:在客户端部署UDPing工具
完成以下操作,在客户端部署UDPing工具。
执行以下命令,下载UDPing工具。
wget https://networktools-public.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/ga/udping/udping.py执行以下命令,赋予UDPing工具执行权限。
chmod +x udping.py
步骤三:测试加速效果
登录客户端。
执行
./udping.py <后端服务器IP> <监听端口>,查看未使用全球加速客户端访问后端服务器的网络延迟。执行
./udping.py <加速IP> <监听端口>,查看使用全球加速后客户端通过加速IP访问后端服务器的网络延迟。图 1. 未使用全球加速,客户端访问后端服务器的网络延迟
全球加速的加速效果以您的实际业务测试为准。
加速IP是您添加加速区域后为加速地域分配的加速IP。
下图以上海到美国(弗吉尼亚)的加速效果作为示例。
图 1. 未使用全球加速,客户端访问后端服务器的网络延迟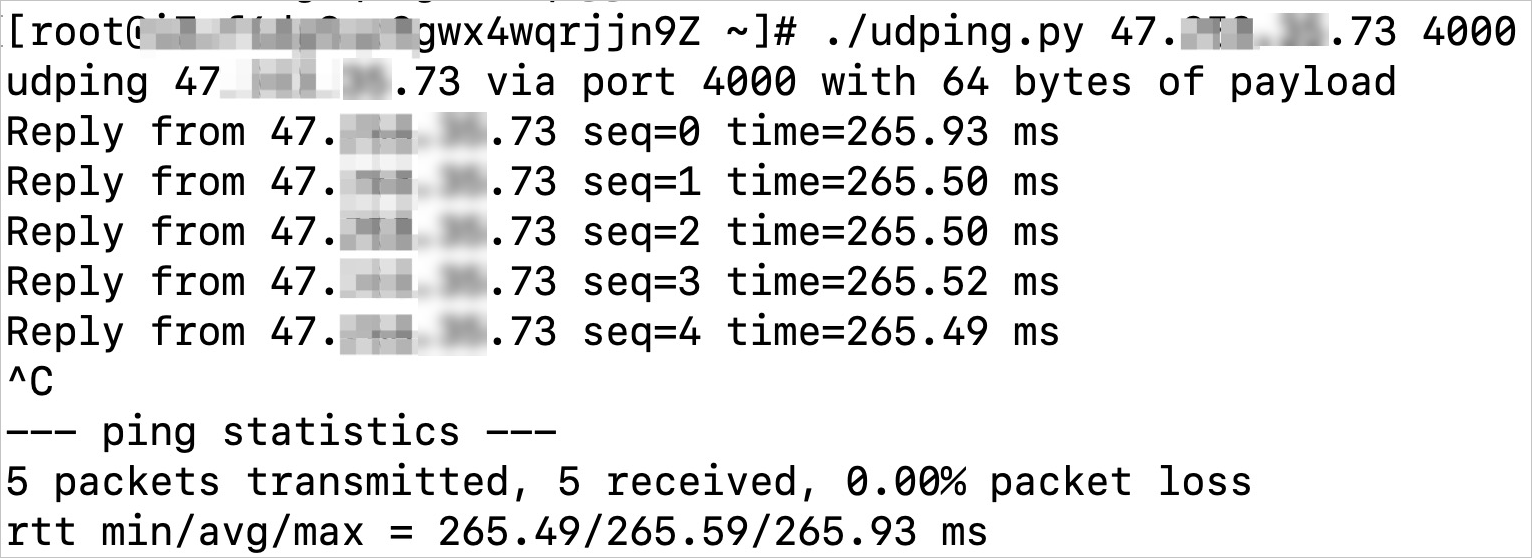
图 2. 使用全球加速后,客户端通过加速IP访问后端服务器的网络延迟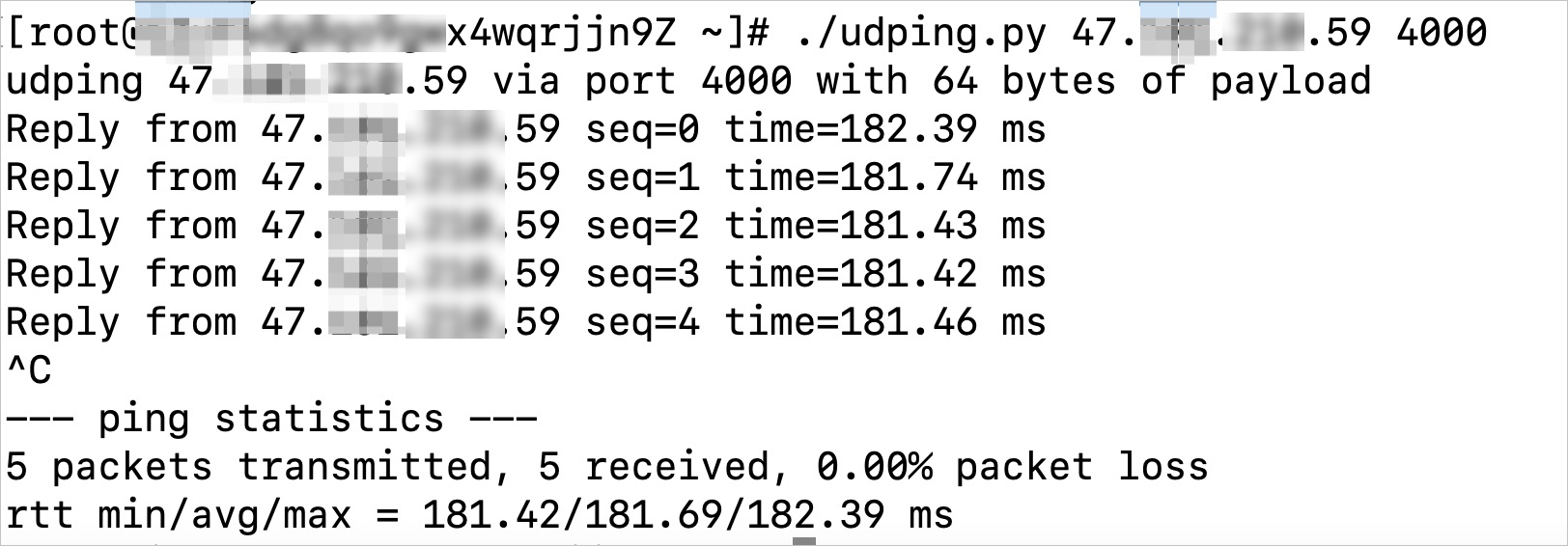
推荐本站淘宝优惠价购买喜欢的宝贝:
本文链接:https://hqyman.cn/post/8598.html 非本站原创文章欢迎转载,原创文章需保留本站地址!
休息一下~~



 微信支付宝扫一扫,打赏作者吧~
微信支付宝扫一扫,打赏作者吧~